STEAM: Bridging Creativity and Innovation for 21st-Century Student Success
)
Just 15 years ago, STEM education was a rare sight, confined to a handful of magnet schools and pilot programs. But today, it's a cornerstone of K-12 learning, empowering students with the skills they need to thrive in the 21st century. The origin of STEM at that time was limited to magnet schools and pilot programs.
The STEM movement has exploded in recent years, with over 13,000 school districts across the US embracing its principles. And many have taken it a step further, integrating the arts to create a more holistic and engaging learning experience known as STEAM. In the early 2000s, educators began to recognize that something was missing from STEM education. The arts, with their focus on creativity and innovation, offered a vital complement to the technical skills emphasized in STEM. The idea of STEAM was born. In 2006, an artist, designer and educator named John Maeda – then-president of the Rhode Island School of Design (RISD) – began advocating for a new model of STEM that fully integrated the arts as a fifth, essential component of the student experience. Under his leadership, RISD actively began promoting STEAM as the newest educational framework.
In 2009, the term STEAM was officially coined, with the arts officially recognized as a critical component that could enrich and enhance STEM programming. This caused a marked shift in the way policymakers and educational institutions viewed the role of the arts; it was no longer a peripheral subject, but something that played an integral role in producing well-rounded, innovative thinkers.
States like California, Massachusetts, Ohio and New York have since placed importance on STEAM by launching statewide initiatives that encourage their school districts to adopt STEAM curricula. For example, California's Department of Education now actively supports STEAM programs by providing various grants and resources for bourgeoning districts. And in 2011 leaders in Georgia launched a statewide certification program giving credibility to schools adopting and implementing STEAM curricula.
A Newfound Dynamic: The Impact of STEAM
Why integrate the arts, and how does it transform the K-12 student experience? The rise of STEAM reflects the changing demands of the 21st-century workforce. In a globalized economy driven by innovation, success requires more than just technical skills. It demands creativity, problem-solving, and the ability to think outside the box. By emphasizing STEAM as a curricular framework, schools can help students build the skills necessary to grow and adapt in our ever-changing, globalized economy.
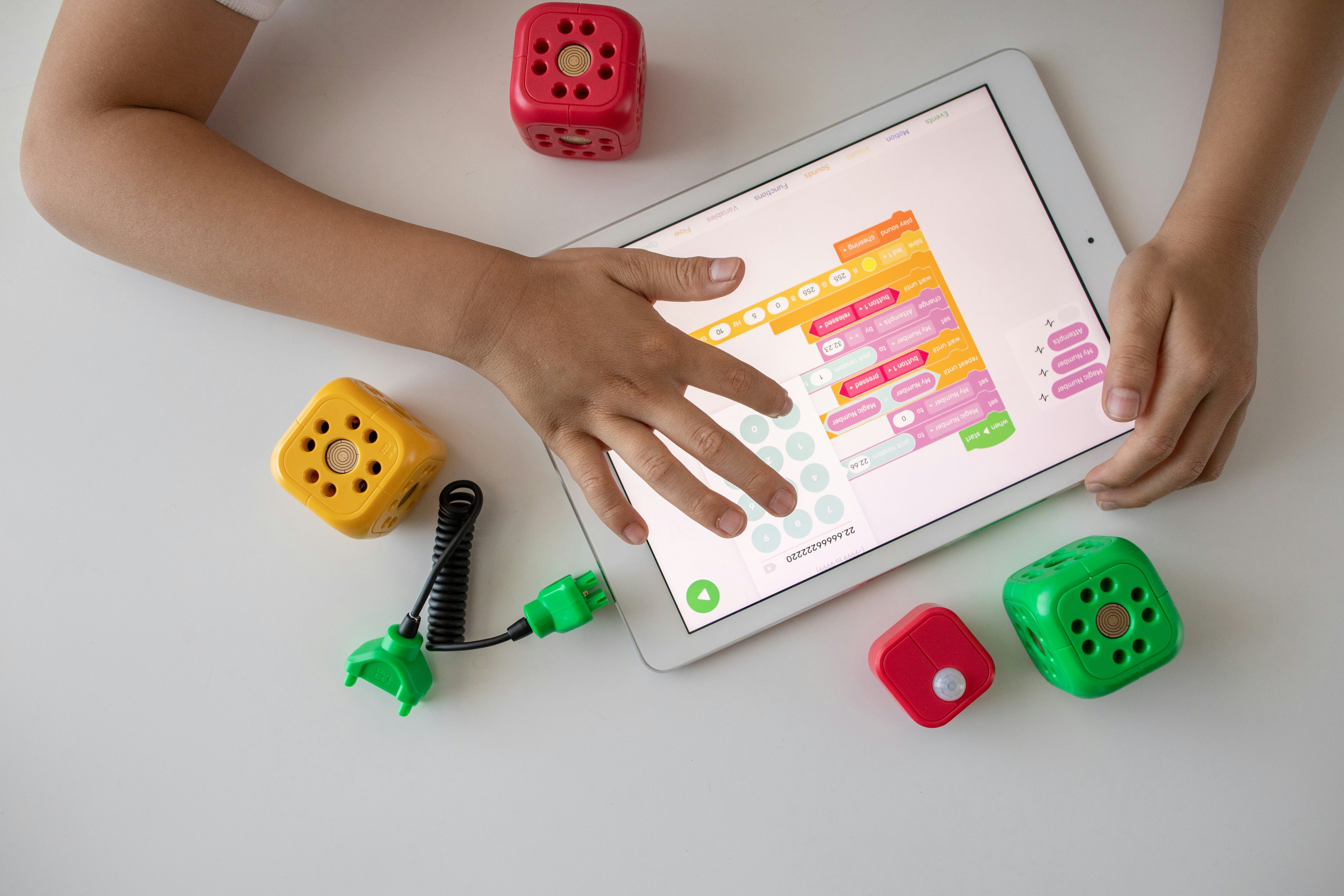

In today's competitive job market, technical skills alone aren't enough. Employers are seeking individuals who are adaptable, creative, and able to collaborate across disciplines. STEAM education fosters these essential qualities, preparing students for the jobs of tomorrow.
- Resilience through Creative Problem-Solving
For example, research indicates that a STEAM-based education can significantly influence students’ ability to build confidence, feel a sense of independence and develop an innovative mindset.
Because a STEAM education emphasizes hands-on, project-based learning, students are statistically more likely to engage in problem-solving activities that involve trial and error. This hands-on learning approach fosters resilience, encouraging students to see failures as valuable opportunities to iterate and refine their solutions.
- Independence through Inquiry-Based Learning
STEAM programs often employ inquiry-based learning, which encourages students to take the lead in exploring topics and questions that interest them.
From designing innovative products to tackling real-world problems, STEAM students learn by doing. They develop critical thinking skills, resourcefulness, and the ability to take initiative, preparing them for the challenges of the 21st century. The autonomy this grants them not only helps students become more adept at solving problems, but also encourages them to become self-directed learners.
- Transferable Skills & Multi-Disciplinary Applications
Finally, a STEAM education can help students build real-world skills that translate to a variety of fields, giving them more flexibility and hire-ability as they enter the workforce. As much as STEAM integrates various technical disciplines, the integration of the arts helps students develop transferable skills like creativity, innovation, and emotional intelligence.
These skills help prepare students to tackle complex, real-world problems beyond the classroom. For instance, a 2020 study by the Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning showed that students who learn to communicate their ideas effectively and collaborate with peers were found to be better equipped to navigate social and academic challenges independently.
STEAM Success: How to Employ STEAM for Continued Student Enrichment
By now you may be asking yourself, “if the arts are so beneficial, then why don’t we hear more about the arts in education?” Well, that’s because STEAM is still a growing concept. But there are quite a few school districts serving as models for their fellow districts to emulate.
One district to see the full benefit of implementing a STEAM education is the Philadelphia School District in Pennsylvania. It garnered national attention for the success of its STEAM After-School Enrichment (ASE) program, due to its innovative integration of the arts into STEM programming.
What sets this program apart is its focus on exploring academic concepts through creative outlets like visual arts, music, dance, and theater. By doing so, the ASE program not only reinforces academic competencies but also nurtures creativity and critical thinking, making learning more dynamic and appealing to students.
It also places a keen focus on engaging students in grades 5-8 in activities that are both fun and educational. Students participate in hands-on projects that help them develop essential skills in literacy, science, math and social-emotional learning. By emphasizing experiential learning, the program bridges abstract concepts with real-world applications, equipping students with both life skills and STEM knowledge.
Finally, because the ASE program offers students the opportunity to engage in various art forms, the it serves as a platform for their cultural and creative enrichment. This aspect of the program has been praised for helping students develop a well-rounded skill set that includes both technical and artistic competencies, preparing them for future academic and career opportunities.
These three core elements have made the Philadelphia School District’s STEAM After-School Enrichment program a standout example of how arts integration can enrich STEM education, ultimately serving as an example well-primed for other districts to follow.
Where Does STEAM Lead Our Students?
We’ve covered how STEAM is beneficial to students’ overall wellbeing and development as well-rounded individuals, but what does it mean for their futures?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, STEM-related fields are projected to grow by 10.8% by 2032, driving increased demand for professionals with multidisciplinary skills.
Advancements in technology, along with the rapid globalization of economies, require the skills developed by STEAM programs that incorporate creative thinking and problem-solving into curriculum.
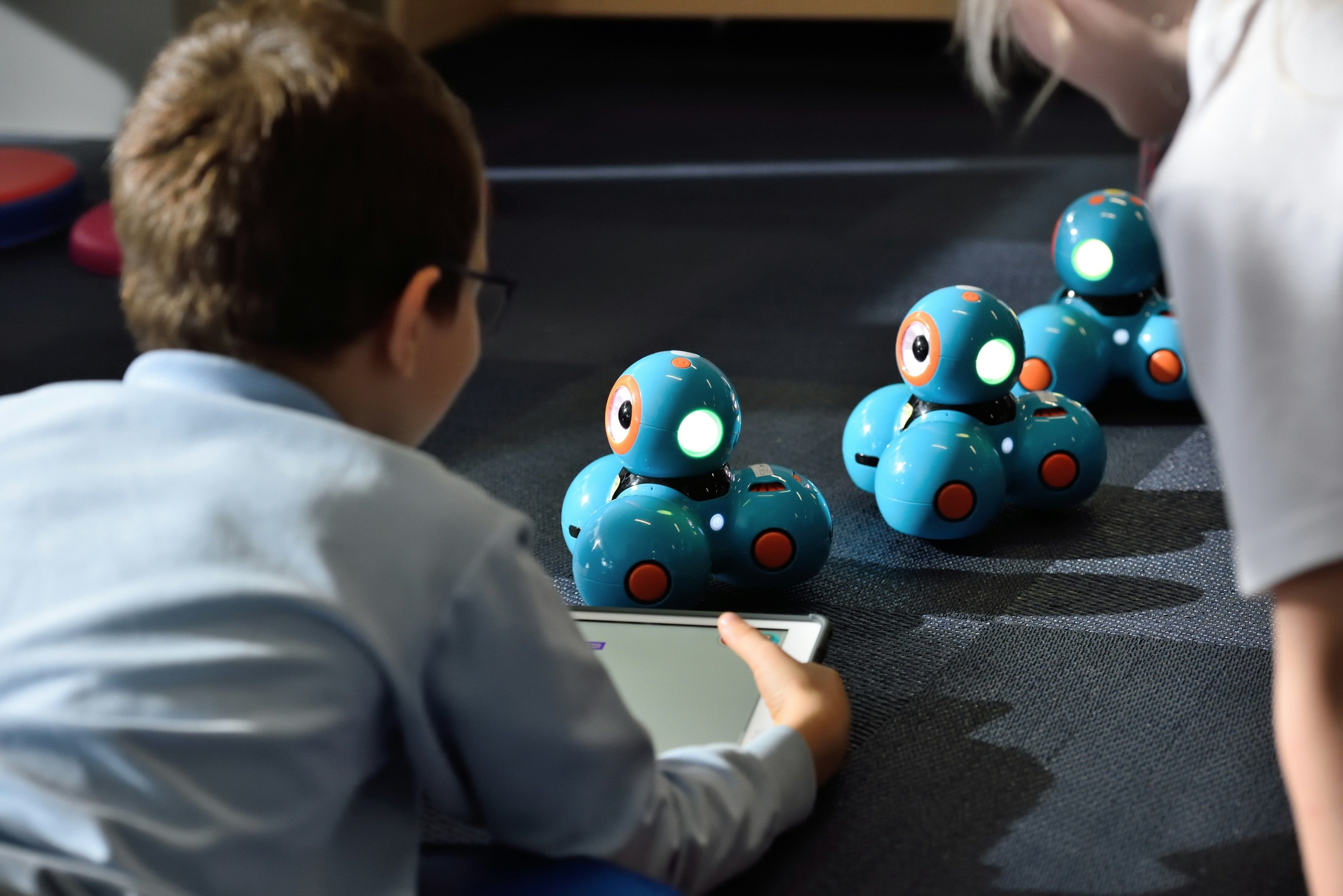

STEAM skills are in high demand across a wide range of industries, including:
- Artificial intelligence (AI), automation and machine learning
- Microbiology, epidemiology, pharmaceutical science and surgery
- Digital illustration, with applications to education, astronomy, medicine, environmental science, global communication and more
- Web development and design
- Data science, analysis and visualization
- User Experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design for the Web, mobile applications and enterprise technologies
- Content creation and development, with applications to business, government and nonprofit organizations
And, according to Amazon and Gallup’s 2023 “Careers of the Future” report, the largest-growing STEAM-related job titles include the following:
- Global business and commerce experts, i.e. project managers, financial analysts, economists, and executive-level business leaders
- Architecture, engineering and construction professionals
- Computer-driven professionals, including user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) designers, software developers and cybersecurity experts
- Medical, environmental science, and health-tech professionals
What Are the Key Takeaways?
Over the past 10 years alone, the STEM framework has grown from a fledgling classroom concept to a must-have for most educational systems around the world. Since adopting the arts as an integral component, STEM became STEAM, further enhancing and complementing the technical skills students gain from the curriculum. The job market of the future is placing higher importance on jobs that require multidisciplinary backgrounds and leaders who possess technical creativity and innovative thinking. Ultimately, STEAM is rapidly emerging as a cornerstone of modern K-12 education, enriching the student experience in innovative and exciting ways.
Ready to Level Up Your Knowledge?
Register for FETC 2025 to dive deeper into STEAM and other cutting-edge topics that are shaping the future of education. Don’t miss out—secure your spot today!










